UCAN for Mental Performance: How Nutrition Impacts Cognitive Function

Introduction:
In the pursuit of optimal mental performance, we often focus on activities like brain training, mindfulness exercises, and adequate sleep. While these practices are undoubtedly essential, one crucial factor that sometimes gets overlooked is nutrition. The food we eat plays a significant role in supporting cognitive function, and certain nutritional choices can have a profound impact on our mental clarity, focus, and overall brain health. In this blog post, we'll explore the relationship between nutrition and cognitive function, with a specific focus on how UCAN products can enhance mental performance.
Understanding Cognitive Function:
Before delving into the role of nutrition, let's briefly discuss what cognitive function entails. Cognitive function refers to the mental processes that enable us to perceive, understand, remember, and apply information. These processes include attention, memory, language, problem-solving, and decision-making. Optimal cognitive function is vital for various aspects of daily life, including work, education, and personal relationships.
The Impact of Nutrition on Cognitive Function:
Numerous studies have demonstrated the link between nutrition and cognitive function. Certain nutrients play key roles in brain health, acting as fuel for neurotransmitter synthesis, supporting neuroplasticity, and protecting against oxidative stress and inflammation. Conversely, poor dietary choices, such as excessive consumption of processed foods and sugar, have been associated with cognitive decline and an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
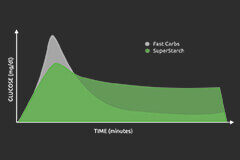
One essential aspect of nutrition that influences cognitive function is blood sugar regulation. Fluctuations in blood glucose levels can affect cognitive performance, mood, and energy levels. High-glycemic foods cause rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar, leading to feelings of fatigue and mental fog. In contrast, low-glycemic foods provide sustained energy without disrupting blood sugar levels, thereby promoting stable cognitive function.
UCAN and Cognitive Performance:
UCAN offers a range of products formulated with SuperStarch, a patented carbohydrate derived from non-GMO corn. Unlike traditional carbohydrates, SuperStarch is unique in its ability to deliver a steady and prolonged release of glucose into the bloodstream, resulting in sustained energy levels without the typical spikes and crashes associated with high-glycemic carbohydrates.
Research has shown that consuming UCAN products can have positive effects on cognitive performance due to their low-glycemic nature and sustained energy release. A study published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition found that athletes who consumed UCAN SuperStarch experienced improved cognitive function and mood compared to those who consumed a high-glycemic carbohydrate drink.
Furthermore, UCAN products are rich in electrolytes, vitamins, and minerals that support overall brain health and function. Electrolytes such as potassium and magnesium play crucial roles in nerve transmission and cognitive processing, while B vitamins are essential for neurotransmitter synthesis and energy metabolism.
Practical Applications and Recommendations:
Incorporating UCAN products into your daily routine can be a simple yet effective way to support cognitive function and mental performance. Whether you're preparing for a demanding workday, a study session, or a challenging workout, UCAN offers a convenient and nutritious solution
Here are some practical tips for maximizing the cognitive benefits of UCAN:
- Start your day with a UCAN SuperStarch-based breakfast to provide sustained energy and mental clarity throughout the morning.
- Keep UCAN bars or powder packets on hand for quick and easy snacks when you need a cognitive boost between meals.
- Use UCAN as a pre-workout supplement to enhance focus, concentration, and endurance during exercise sessions.
- Stay hydrated by consuming UCAN Hydrate, a low-calorie electrolyte drink that supports hydration and cognitive function.
Conclusion:
Optimizing cognitive function requires a multifaceted approach that includes adequate sleep, regular exercise, stress management, and, importantly, proper nutrition. By choosing nutrient-dense foods like UCAN products that support stable blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients for brain health, you can fuel your mind for peak performance in all aspects of life. Make UCAN a part of your daily routine and experience the cognitive benefits firsthand. Your brain will thank you for it.
References:
- Koenig et al. (2017). Improved cognitive function and mental endurance in a multi-ingredient energy supplement compared to caffeine alone: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14(1), 38.
- Gershuni et al. (2020). UCAN: A SuperStarch® Designed to Optimize Blood Sugar and Athletic Performance. Frontiers in Nutrition, 7, 610798.
Glycemic Index Comparison Table:
| Carbohydrate Source | Glycemic Index (GI) | Effect on Cognitive Function |
|---|---|---|
| UCAN SuperStarch | Low (~29) | Provides sustained energy without spikes and crashes, supporting stable cognitive function and mood. |
| Rolled Oats | Medium (~55) | Offers moderate energy release but may cause a slight increase in blood sugar levels, potentially leading to fluctuations in cognitive performance. |
| White Bread | High (~70) | Causes rapid spikes in blood sugar followed by crashes, leading to fatigue, mental fog, and decreased cognitive function. |
| Bananas | Medium (~51) | Provides moderate energy and contains beneficial nutrients like potassium, but may lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels for some individuals. |
| Table Sugar (Sucrose) | High (~65) | Results in rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, followed by a sharp decline, negatively impacting cognitive function and mood. |
| Sweet Potatoes | Medium (~61) | Offers sustained energy and contains vitamins and minerals beneficial for brain health, but may cause slight fluctuations in blood sugar levels. |